React-router
react 路由
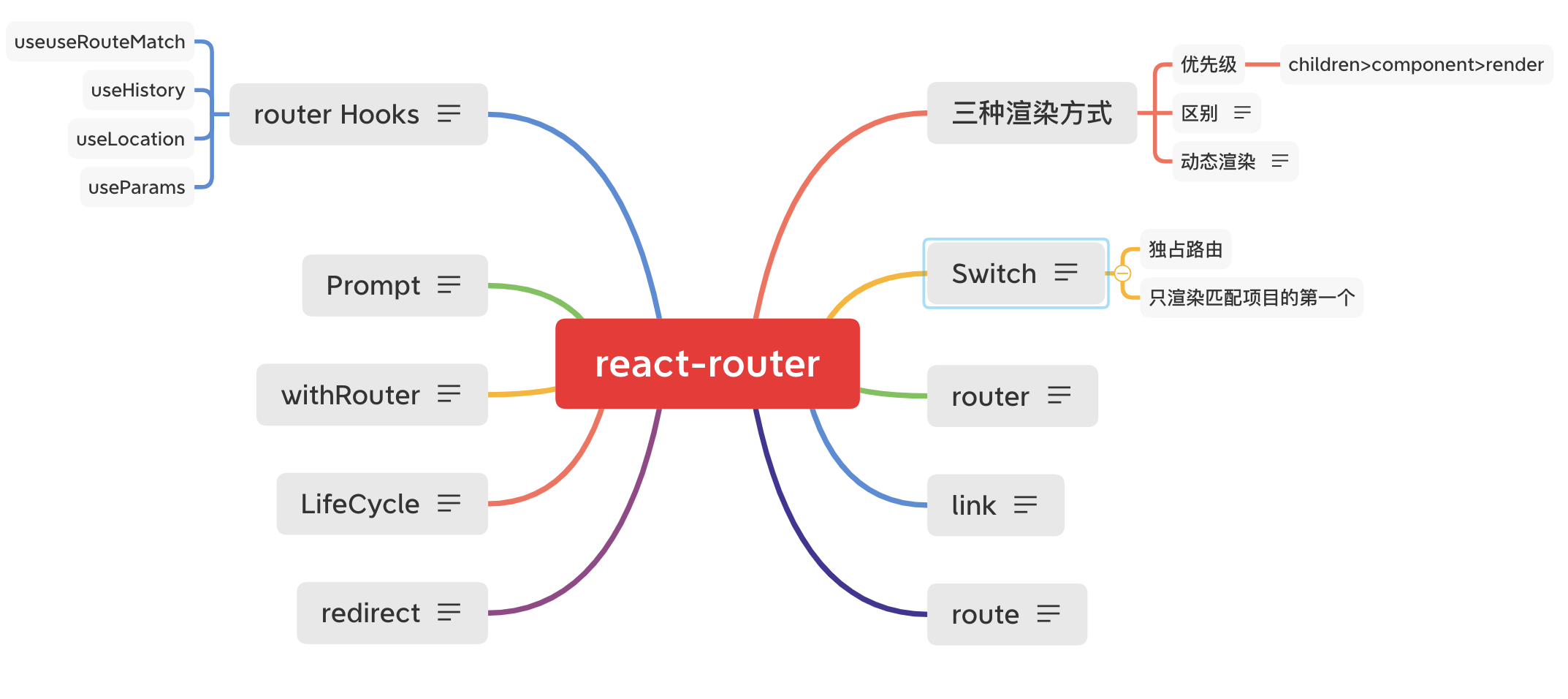
三种渲染方式
渲染优先级
children>component>render
区别
children 无论何时都会被渲染 component 和 render 只有匹配的时候才会被渲染
jsx
/* 渲染component的时候会调用React.createElement,如果使用下面这种匿名函数的形式,每次都会生成一个新的匿名的函数,导致生成的组件的type总是不相同,这个时候会产生重复的卸载和挂载 */
<Route component={() => <Child count={count} />} /> <Route component={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />} />
/* 正确的示范 */
<Route render={() => <Child count={count} />} />
<Route render={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />/>
/* children */
<Route children={() => <FunctionChild count={count} />} />Route
核心组件,注册每一个路由组件
jsx
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./Context";
import matchPath from "./matchPath";
export default class Route extends Component {
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
const location = context.location;
const { path, children, component, render } = this.props;
const match = this.props.computedMatch
? this.props.computedMatch
: path
? matchPath(location.pathname, this.props)
: context.match;
const props = {
...context,
match,
};
// match 渲染三者之一 children(function或者节点) component render或者null
// 不match 渲染children(function)或者null
//return match ? React.createElement(component) : null;
return (
<RouterContext.Provider value={props}>
{match
? children
? typeof children === "function"
? children(props)
: children
: component
? React.createElement(component, props)
: render
? render(props)
: null
: typeof children === "function"
? children(props)
: null}
</RouterContext.Provider>
);
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}Switch
独占路由,处理子组件,传入新的复合组件
jsx
export default class Switch extends Component {
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
const { location } = context;
let match = undefined; //匹配的match
let element = undefined; //匹配的元素
// todo 遍历children,给匹配赋值 done
// 找到第一个匹配的Route或者Redirect
// 这里写React.Children就是因为我不想判断children的数据类型,课下去官网看下React.Children的用法
React.Children.forEach(this.props.children, (child) => {
// child 是Route或者Redirect
if (match == null && React.isValidElement(child)) {
element = child;
const { path } = child.props;
match = path
? matchPath(location.pathname, child.props)
: context.match;
}
});
return match
? React.cloneElement(element, {
computedMatch: match,
})
: null;
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}Router
路由管理者,computeRootMatch 处理无路由匹配的情况,在独占路由中,优先级会被降低,不会出现不写路由始终渲染的情况
js
export default class Router extends Component {
static computeRootMatch(pathname) {
return { path: "/", url: "/", params: {}, isExact: pathname === "/" };
}
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
location: props.history.location,
};
// 监听location变化
this.unlisten = props.history.listen((location) => {
this.setState({ location });
});
}
componentWillUnmount() {
// 取消监听
if (this.unlisten) {
this.unlisten();
}
}
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Provider
value={{
history: this.props.history,
location: this.state.location,
match: Router.computeRootMatch(this.state.location.pathname),
}}
>
{this.props.children}
</RouterContext.Provider>
);
}
}Link
本质上就是一个 link,禁用了默认跳转。通过上下文的 history 进行跳转。需要使用 history 库。
jsx
export default class Link extends Component {
static contextType = RouterContext;
handleClick = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
// 手动跳转
this.context.history.push(this.props.to);
};
render() {
const { children, to, ...restProps } = this.props;
return (
<a href={to} {...restProps} onClick={this.handleClick}>
{children}
</a>
);
}
}Redirect
重定向
jsx
import React, { Component } from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./Context";
import LifeCycle from "./LifeCycle";
export default class Redirect extends Component {
// ! render是要返回ui的,也就是当前组件的子节点,你跳转走了,就没了children了
render() {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
const { to, push = false } = this.props;
return (
<LifeCycle
onMount={() => {
push ? context.history.push(to) : context.history.replace(to);
}}
/>
);
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}
}LifeCycle
jsx
import React, { Component } from "react";
export default class LifeCycle extends Component {
componentDidMount() {
if (this.props.onMount) {
this.props.onMount.call(this, this);
}
}
render() {
return null;
}
}withRouter
一个高阶函数,处理 render 方法中的组件无法拿到 routerProps 的问题
js
<Route path="/product/:id" render={() => <Product />} />;
@withRouter
class Product extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { confirm: true };
}
render() {
const { params } = this.props.match;
const { id } = params;
return (
<div>
Product:{id}
/>
</div>
);
}
}js
const withRouter = (WarppedComponent) => (props) => {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
return <WarppedComponent {...props} {...context} />;
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
};Prompt
阻拦方法,在渲染前
jsx
import React from "react";
import { RouterContext } from "./Context";
import LifeCycle from "./LifeCycle";
export default function Prompt({ message, when = true }) {
return (
<RouterContext.Consumer>
{(context) => {
if (!when) {
return null;
}
let method = context.history.block;
return (
<LifeCycle
onMount={(self) => {
self.release = method(message);
}}
>
onUnmount=
{(self) => {
self.release();
}}
</LifeCycle>
);
}}
</RouterContext.Consumer>
);
}Router-hooks
把 context 对象通过 hook 方法传出去
js
import { RouterContext } from "./Context";
import { useContext } from "react";
export function useHistory() {
return useContext(RouterContext).history;
}
export function useLocation() {
return useContext(RouterContext).location;
}
export function useRouteMatch() {
return useContext(RouterContext).match;
}
export function useParams() {
const match = useContext(RouterContext).match;
return match ? match.params : {};
}