Vue核心
生命周期图
- vue 生命周期
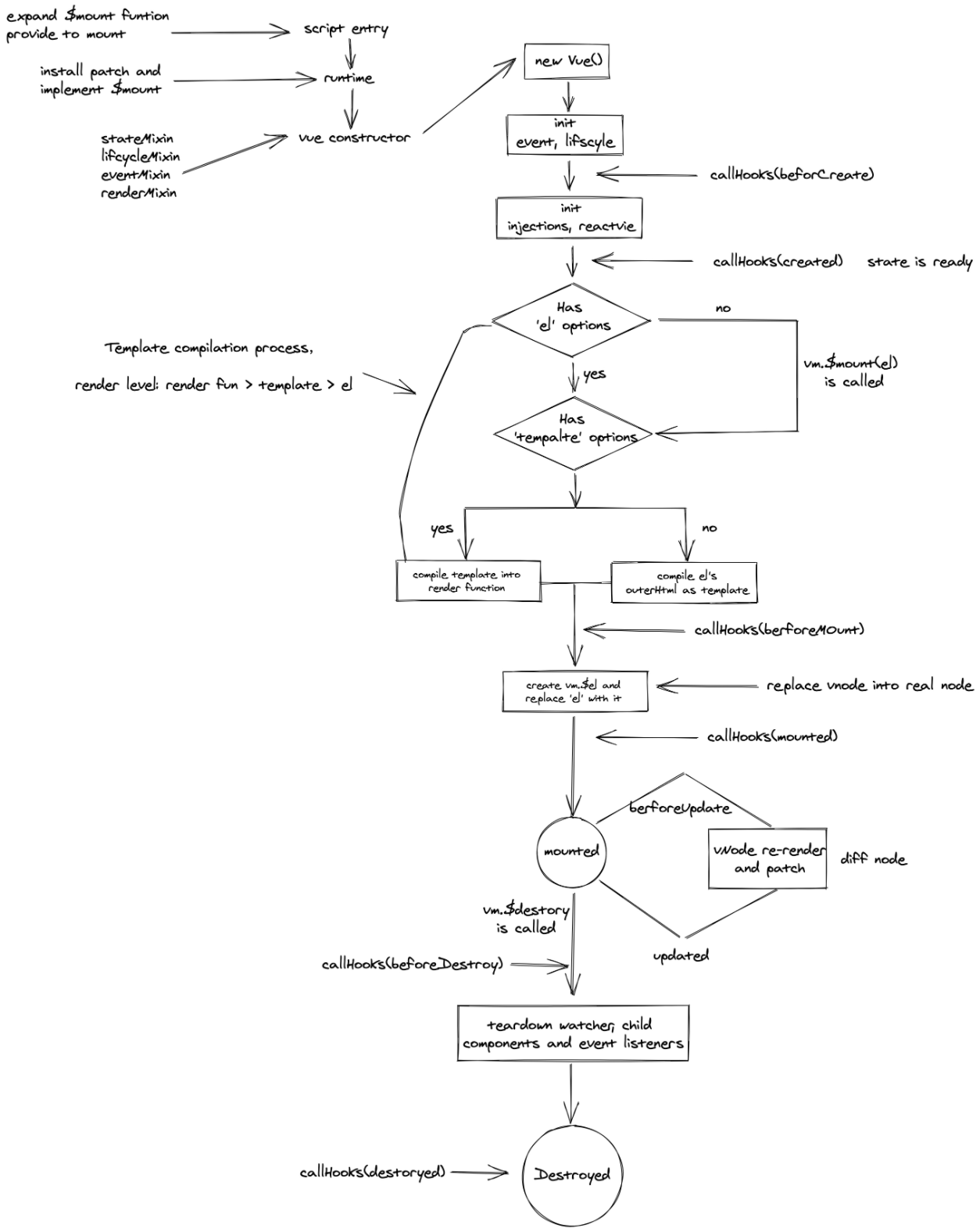
beforeCreate:执行时组件还未创建,通常用于插件开发中执行一些未初始化任务
created:组件初始化完毕,各种数据可以使用,常用于异步数据获取
beforeMounted:未执行渲染,更新,dom 未创建
mounted:初始化结束,dom 创建,可用于获取访问数据和 dom 元素
beforeUpdate:更新前,可用于获取更新前各种状态
updated:更新后,所有状态都是最新
beforeDestory:销毁前,用于定时器或订阅的取消
destoryed:组件已经销毁
运行流程

实例化与入口
流程图
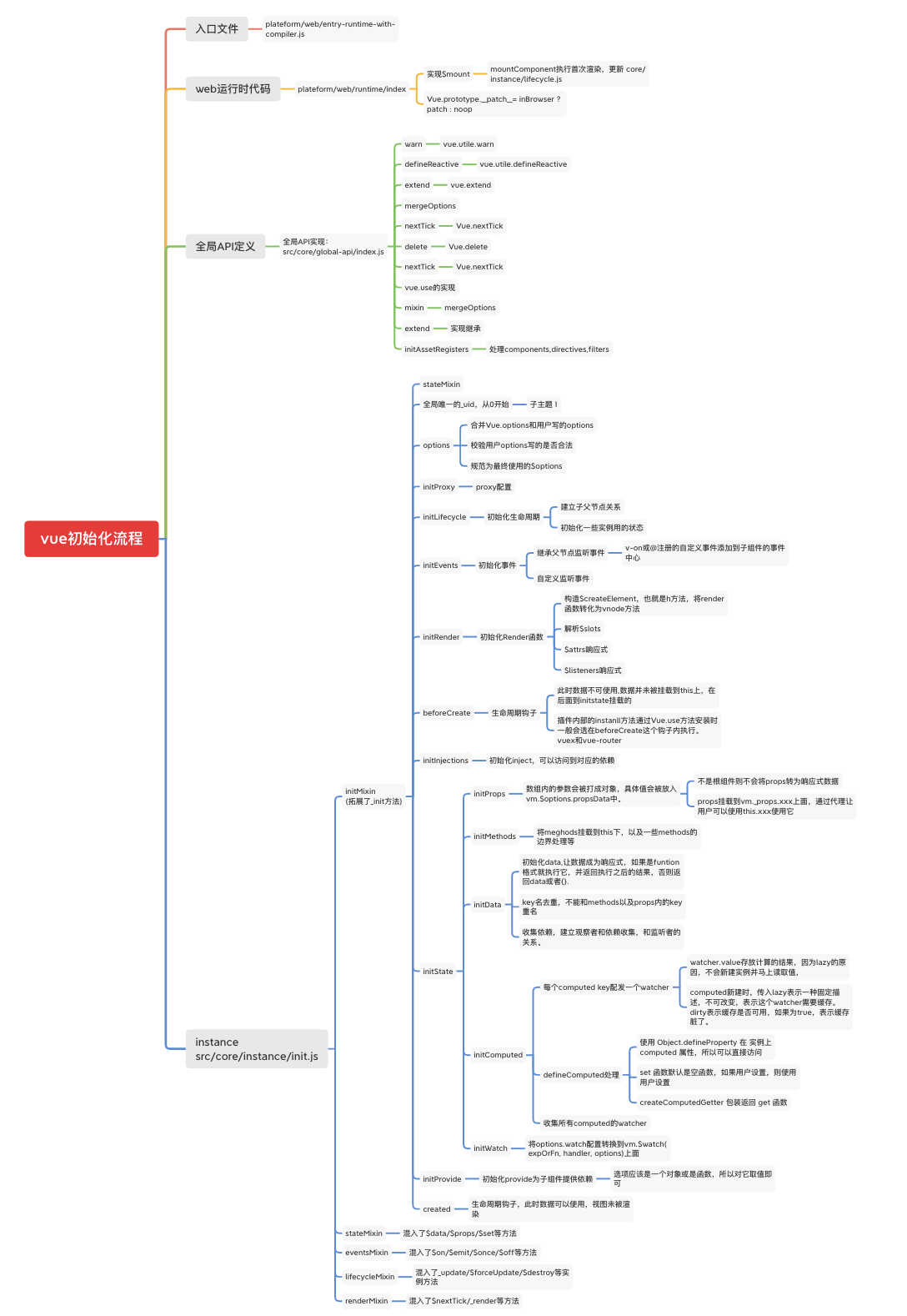
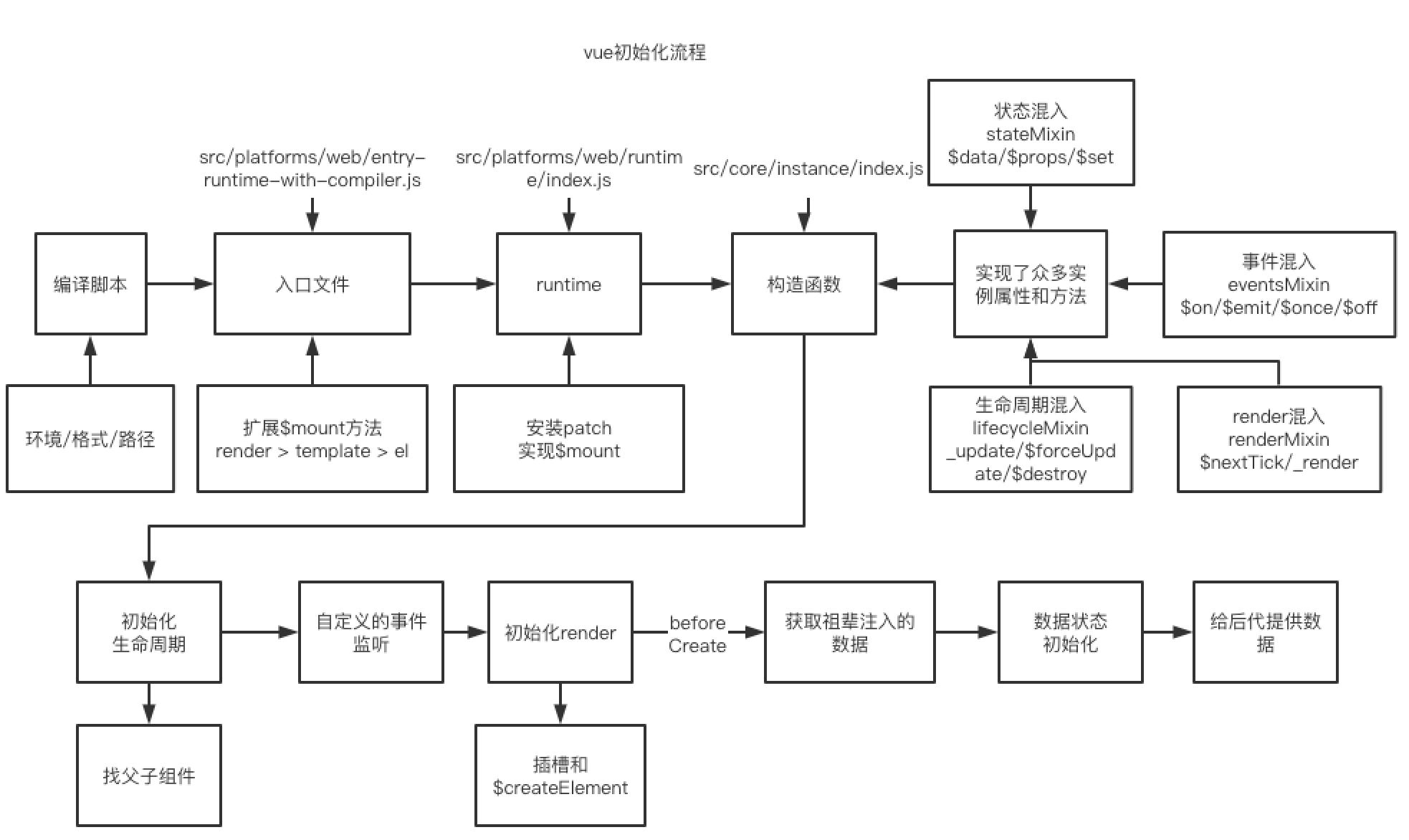
源码入口文件,做了初始化工作,/instance/index 为vue实例, initGlobalAPI 中为初始化流程。
// src/core/index.js
import Vue from './instance/index'
import { initGlobalAPI } from './global-api/index'
import { isServerRendering } from 'core/util/env'
import { FunctionalRenderContext } from 'core/vdom/create-functional-component'
initGlobalAPI(Vue)
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$isServer', {
get: isServerRendering
})
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$ssrContext', {
get () {
return this.$vnode && this.$vnode.ssrContext
}
})
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'FunctionalRenderContext', {
value: FunctionalRenderContext
})
Vue.version = '__VERSION__'
export default Vue实例文件中定义了一个 Vue Class,然后调用了一系列的 init、mixin这样的方法来初始化功能,这里导出的就是一个vue的功能类。
// core/instance/index
import { initMixin } from './init'
import { stateMixin } from './state'
import { renderMixin } from './render'
import { eventsMixin } from './events'
import { lifecycleMixin } from './lifecycle'
import { warn } from '../util/index'
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue再来看全局 API
export function initGlobalAPI (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
// config
const configDef = {}
configDef.get = () => config
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
configDef.set = () => {
warn(
'Do not replace the Vue.config object, set individual fields instead.'
)
}
}
Object.defineProperty(Vue, 'config', configDef)
// 这些工具方法不视作全局API的一部分,除非你已经意识到某些风险,否则不要去依赖他们
Vue.util = {
warn,
extend,
mergeOptions,
defineReactive
}
// 这里定义全局属性
Vue.set = set
Vue.delete = del
Vue.nextTick = nextTick
Vue.options = Object.create(null)
ASSET_TYPES.forEach(type => {
Vue.options[type + 's'] = Object.create(null)
})
Vue.options._base = Vue
extend(Vue.options.components, builtInComponents)
// 定义全局方法
initUse(Vue)
initMixin(Vue)
initExtend(Vue)
initAssetRegisters(Vue)
}GlobalAPI 列表
- 【Vue.config】 各种全局配置项
- 【Vue.util】 各种工具函数,还有一些兼容性的标志位
- 【Vue.set/delete】
- 【Vue.nextTick】
- 【Vue.options】
- 【Vue.use】通过initUse方法定义
- 【Vue.mixin】 通过initMixin方法定义
- 【Vue.extend】通过initExtend方法定义
初始化与流程
在引入vue的时候有一系列的混入功能,我们先来研究一下 initMixin 中发生了什么。
// core/instance/init.js
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
const vm: Component = this
vm._uid = uid++
let startTag, endTag
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
startTag = `vue-perf-start:${vm._uid}`
endTag = `vue-perf-end:${vm._uid}`
mark(startTag)
}
// 如果是Vue的实例,则不需要被observe
vm._isVue = true
// 内部组件的话直接处理
if (options && options._isComponent) {
initInternalComponent(vm, options)
} else {
// 根组件走mergeOptions
vm.$options = mergeOptions(
resolveConstructorOptions(vm.constructor),
options || {},
vm
)
}
// 第二步: 初始化组件的代理
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
initProxy(vm)
} else {
vm._renderProxy = vm
}
vm._self = vm
// 第三步: 初始化生命周期
initLifecycle(vm)
// 第四步:初始化事件监听
initEvents(vm)
// 初始化渲染函数
initRender(vm)
// beforeCreate生命周期
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
// 初始化state
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
// created生命周期
callHook(vm, 'created')
// 组件挂载
if (vm.$options.el) {
vm.$mount(vm.$options.el)
}
}
}mergeOptions的实现,根示例与非根示例走不同的逻辑
export function mergeOptions (
parent: Object,
child: Object,
vm?: Component
): Object {
//...
// 统一props格式
normalizeProps(child)
// 统一directives的格式
normalizeDirectives(child)
// 针对不同的键值,采用不同的merge策略
const options = {}
let key
for (key in parent) {
mergeField(key)
}
for (key in child) {
if (!hasOwn(parent, key)) {
mergeField(key)
}
}
function mergeField (key) {
const strat = strats[key] || defaultStrat
options[key] = strat(parent[key], child[key], vm, key)
}
return options
}options.data经过merge之后,实际上是一个function,在真正调用function才会进行真正的merge,其它的merge都会根据自身特点而又不同的操作.
renderProxy
renderProxy 是后期为render做准备的,一般而言,vm._renderProxy是等于vm的,在非生产环境中,Vue动用了Proxy,也是vue3的核心理念之一。
initLifecycle
合并完参数之后继续往下走流程,initLifecycle。
export function initLifecycle (vm: Component) {
const options = vm.$options
// 这里判断是否存在父示例,如果存在,则通过 while 循环,建立所有组建的父子关系
let parent = options.parent
if (parent && !options.abstract) {
while (parent.$options.abstract && parent.$parent) {
parent = parent.$parent
}
parent.$children.push(vm)
}
/**
* 为组件实例挂载相应属性,并初始化
*/
vm.$parent = parent
vm.$root = parent ? parent.$root : vm
vm.$children = []
vm.$refs = {}
vm._watcher = null
vm._inactive = null
vm._directInactive = false
vm._isMounted = false
vm._isDestroyed = false
vm._isBeingDestroyed = false
}这边分两步,一步是建立组件的父子关系,另一部分是初始化组件示例。
initEvents
我们常用的事件$on, $once, $off, $emit, 都在此进行挂载
export function initEvents (vm: Component) {
vm._events = Object.create(null)
vm._hasHookEvent = false
// init parent attached events
const listeners = vm.$options._parentListeners
if (listeners) {
updateComponentListeners(vm, listeners)
}
}initRender
initRender挂载了_render私有方法,它用来把实例渲染成一个vNode。初始化一些渲染属性,比如 $slots 和 $createElement 等。
渲染过程
<div id="app">
{{ message }}
</div>通过render函数
render: function (createElement) {
return createElement('div', {
attrs: {
id: 'app'
},
}, this.message)
}initInjections 和 initProvide
initInjections 和 initProvide的执行顺序:
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/propsinitState
这里的主要工作主要是定义的数据进行defineReactive. 主要是 props 和 data
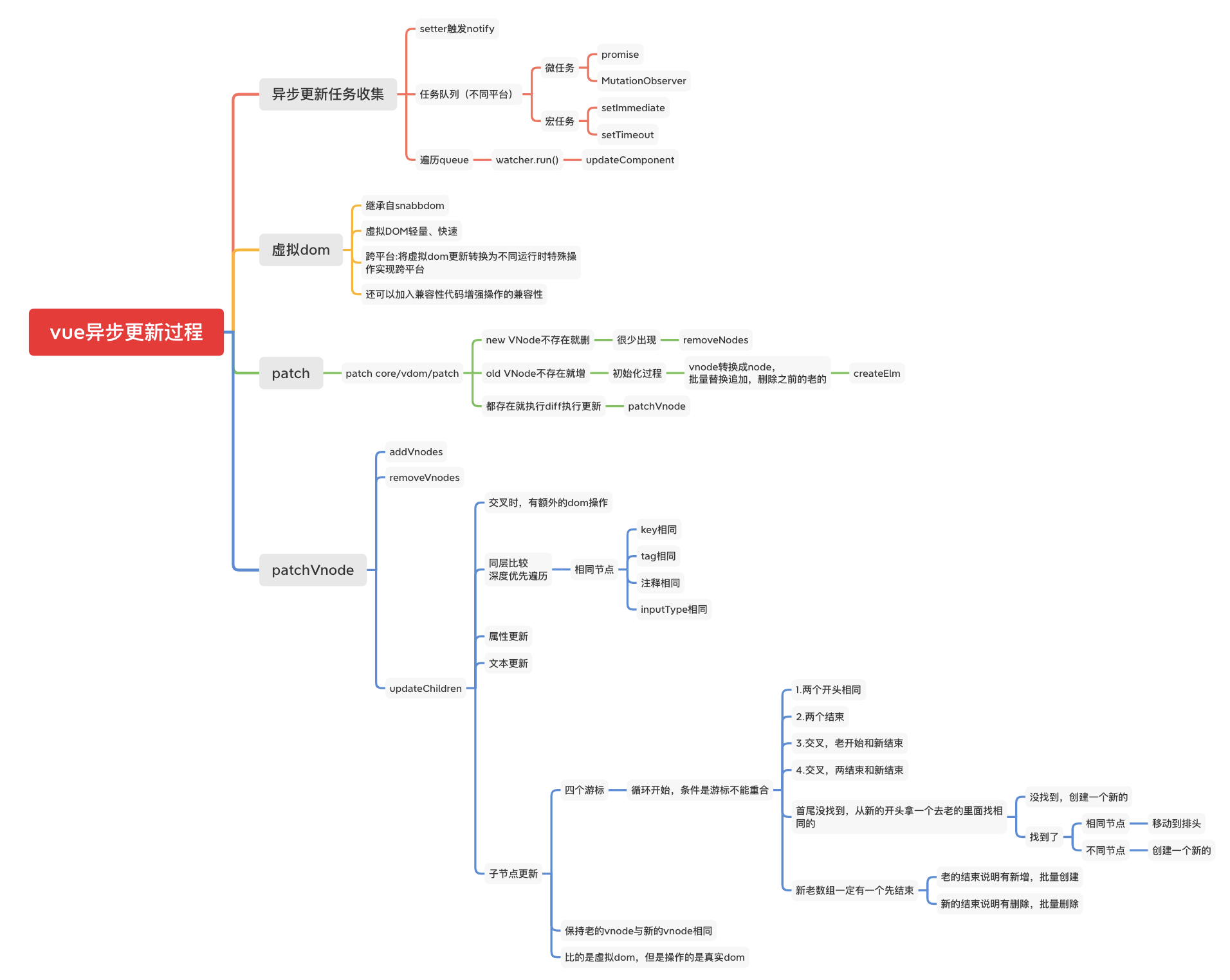
异步更新
组件化流程
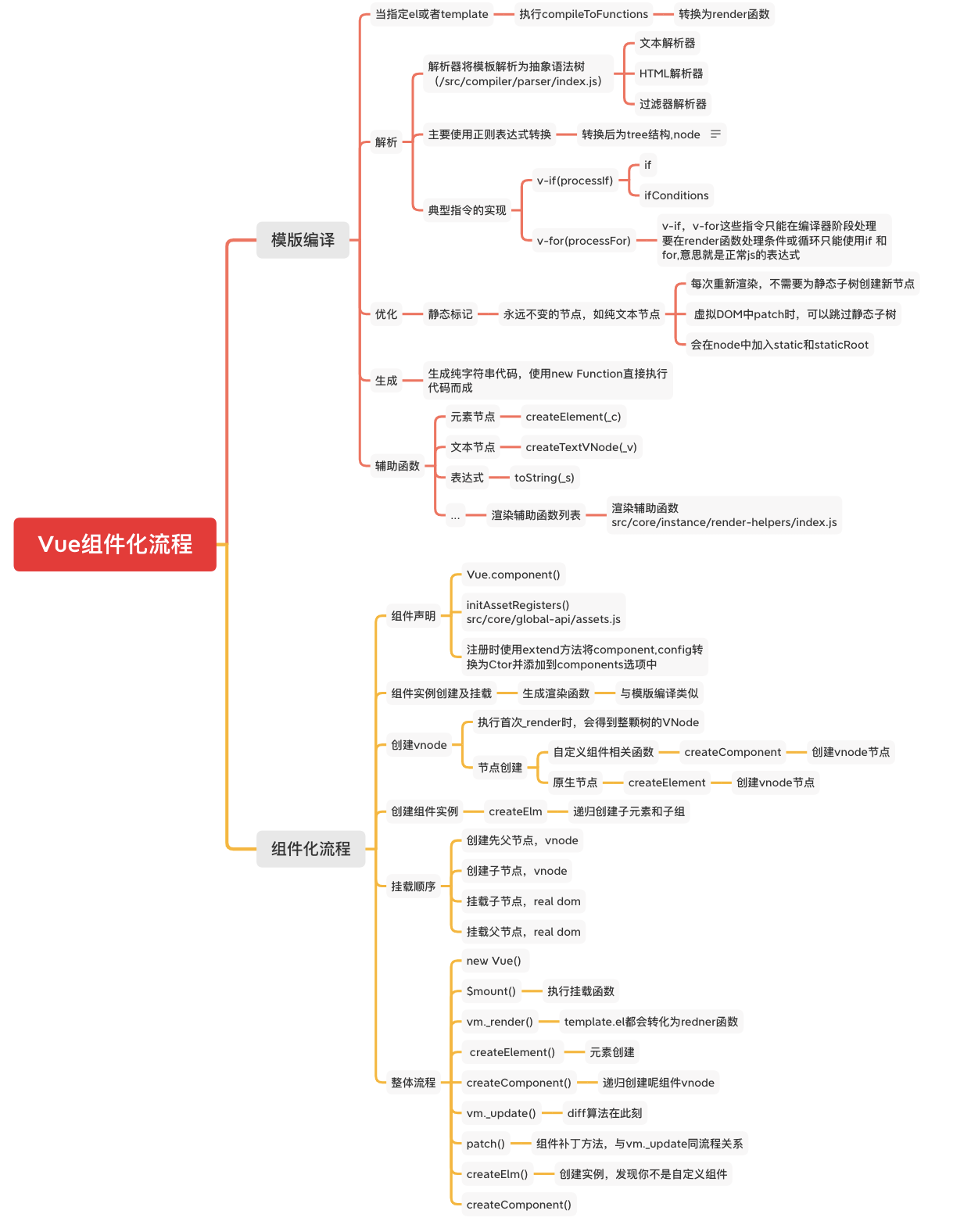
事件系统
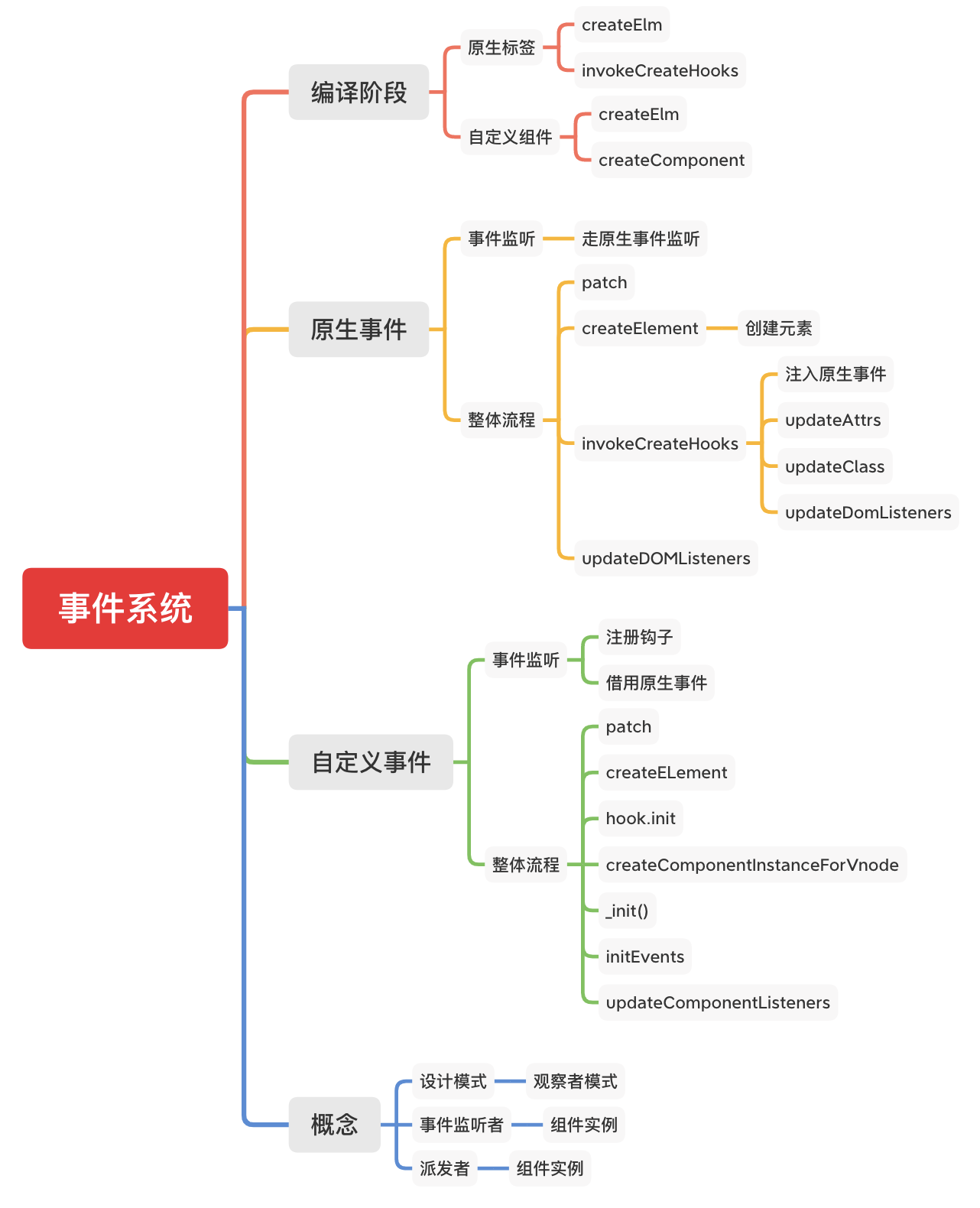
vue2.0 数据响应式
数据响应式过程 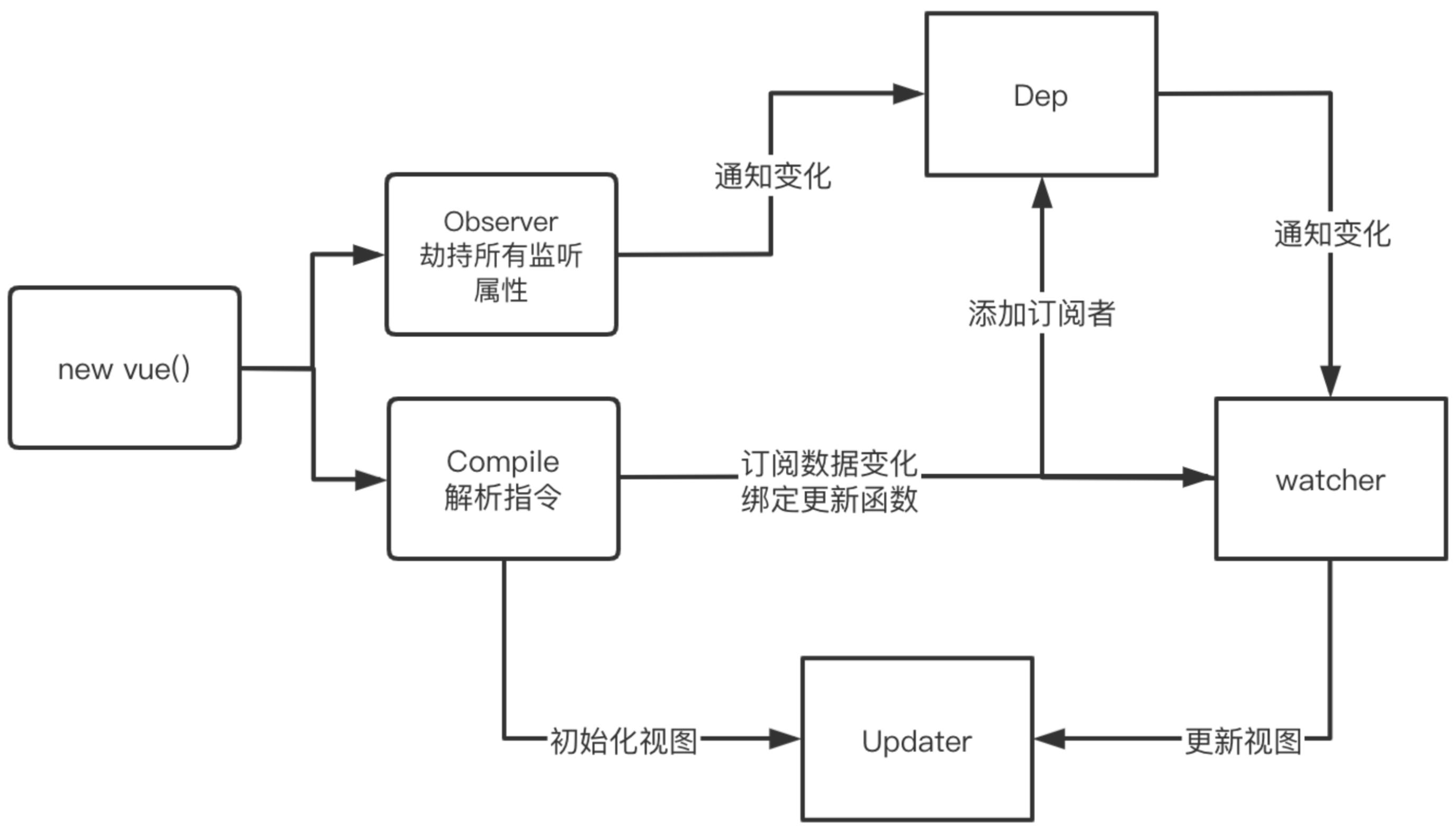
- MyVue:框架构造函数
- Observer:执⾏数据响应化(分辨数据是对象还是数组)
- Compile:编译模板,初始化视图,收集依赖(更新函数、watcher 创建)
- Watcher:执⾏更新函数(更新dom)
- Dep:依赖,管理多个 Watcher,批量更新
流程描述
数据劫持
- 将data做响应式处理,走reactive
- 递归的对对象做处理
- 创建依赖对象,每一个key一个依赖对象
代理data
- 代理data,将data的值映射到vm上
编译过程
- 指令编译,遍历子元素等
- 遇到响应式对象,确认update函数,创建wathcer,并将watcher添加到相应key到依赖队列中
响应式处理
- 修改响应式数据后,触发依赖对象的notify,遍历执行watcher中的更新函数,达到更新效果
响应式核心代码
function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
// 如果val是对象,需要递归处理之
observe(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
return val
},
set(newVal) {
if(val !== newVal) {
// 如果newVal是对象,也要做响应式处理
observe(newVal)
val = newVal
}
}
})
}
// 遍历指定数据对象每个key,拦截他们
function observe(obj) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj === null) {
return obj
}
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
defineReactive(obj, key, obj[key])
})
}// 第一步初始化
class PYVue {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options
this.$data = options.data
this.$methods = options.methods
// 让数据成为响应式的数据,观察者
observe(this.$data)
//为$data做代理
proxy(this, '$data')
// 编译
new Compile('#app', this)
}
}数据响应式原理
// 响应式
function defineReactive(obj, key, val) {
// val是对象还需要递归处理
observe(val)
const dep = new Dep()
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
get() {
// 依赖收集
Dep.target && dep.addDep(Dep.target)
return val
},
set(newVal) {
// 如果newVal是对象,也要做响应式处理
if(val && val != newVal) {
observe(newVal)
val = newVal
dep.notify()
}
}
})
}
function observe(obj) {
if (typeof obj !== 'object' || obj !== null) {
return obj
}
if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
obj.__proto__ = arrProto
const keys = Object.keys(obj)
for (let i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
observe(obj[i])
}
} else {
new Observe(obj)
}
}
function proxy(vm, key) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach(k => {
Object.defineProperty(vm, k, {
get() {
return vm[key][k]
},
set(v) {
vm[key][k] = v
}
})
})
}
class Observe {
constructor(val) {
this.val = val
walk(this)
}
// 收集
walk(obj) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
defineReactive(obj, key, obj[key])
})
}
}依赖收集过程
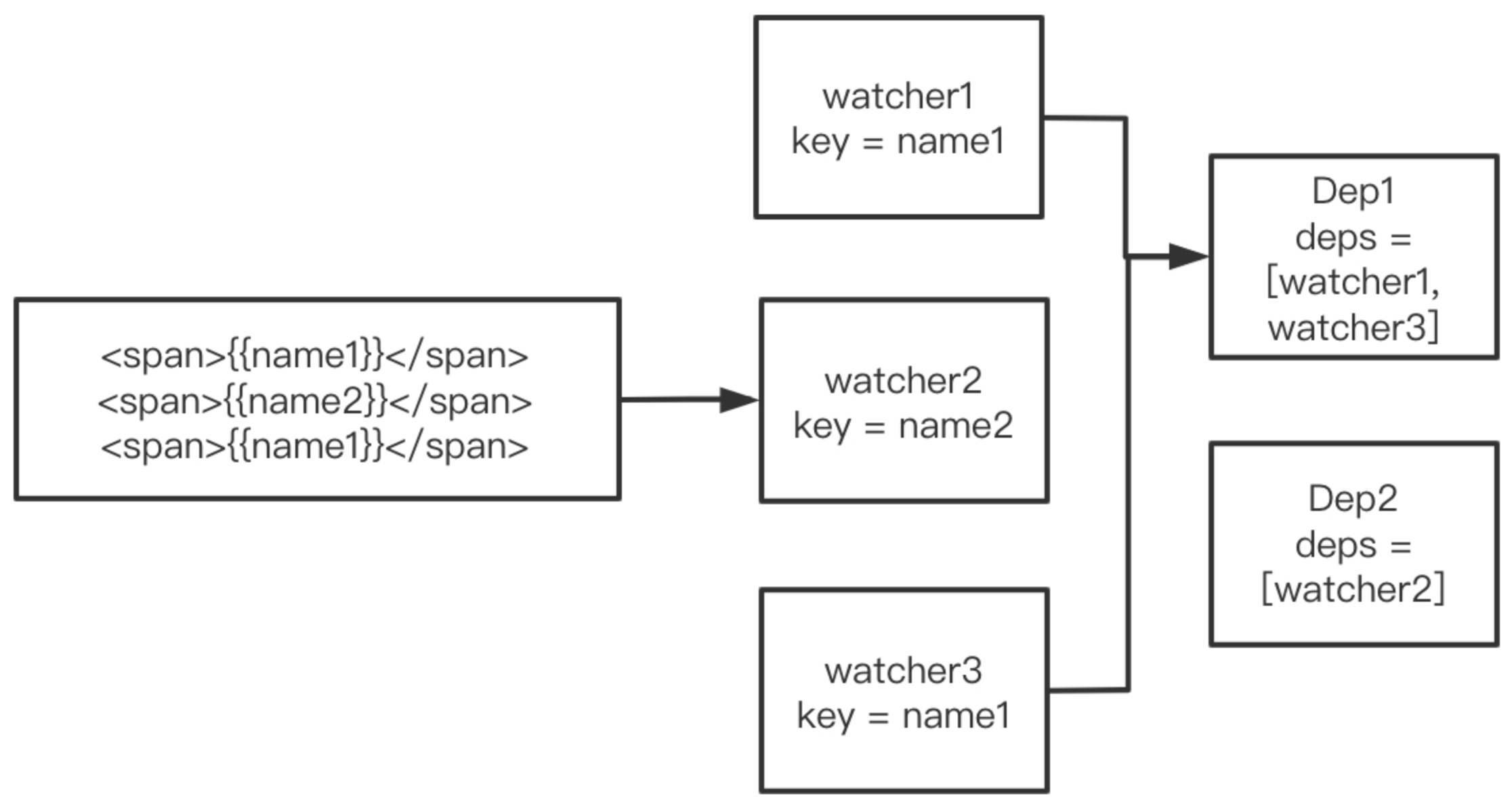
// 监听者
class Watcher {
constructor(vm ,key, updaterFn) {
this.vm = vm
this.key = key
this.updaterFn = updaterFn
Dep.target = this
this.vm[this.key]
Dep.target = null
}
update() {
this.updaterFn.call(this.vm, this.vm[this.key])
}
}
// 收集者
class Dep {
constructor() {
this.deps = []
}
addDep(watcher) {
this.deps.push(watcher)
}
notify() {
this.deps.forEach(watcher => {
watcher.update()
})
}
}模版编译过程
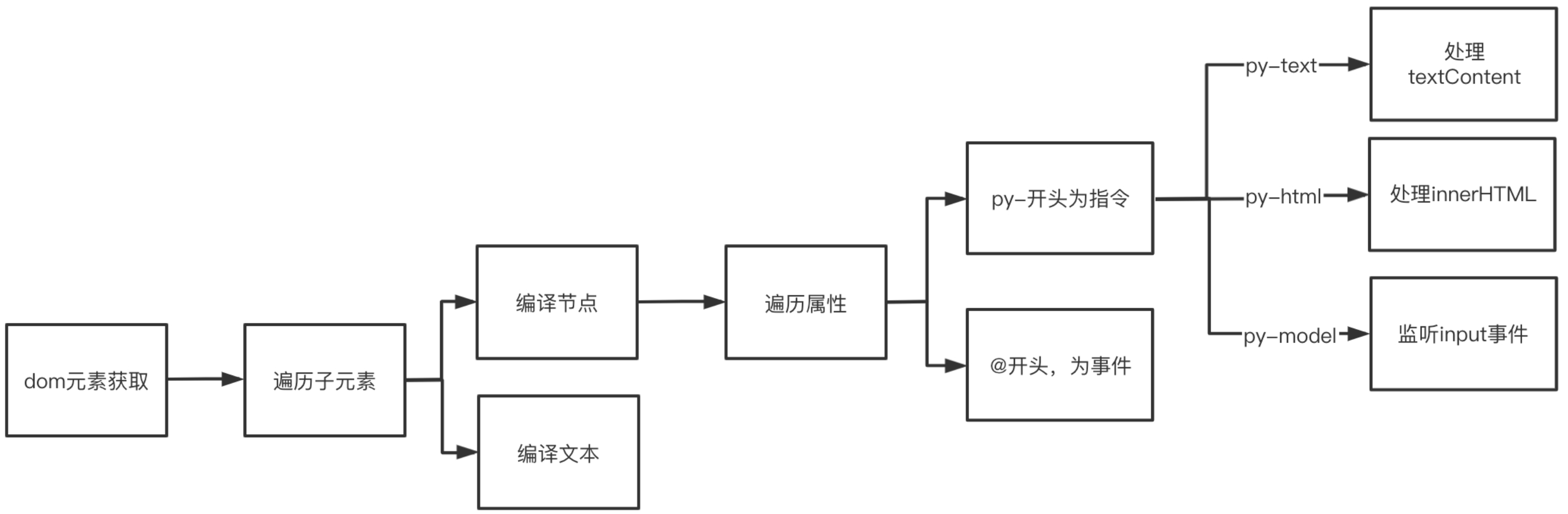
class Compile {
constructor(el, vm) {
this.$el = document.querySelector(el)
this.$vm = vm
if (this.$el) {
this.compile(this.$el)
}
}
compile(el) {
el.childNodes.forEach(node => {
if (node.nodeType == 1) {
this.compileElement(node)
} else if (this.isInter(node)) {
this.compileText(node)
}
if(node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length > 0) {
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
isInter(node) {
return node.nodeType === 3 && /\{\{(.*)\}\}/.test(node.textContent)
}
compileText(node) {
this.update(node, RegExp.$1, 'text')
}
compileElement(node) {
const nodeAttrs = node.attributes
Array.from(nodeAttrs).forEach(attr => {
const attrName = attr.name
const exp = attr.value
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
const dir = attrName.substring(3)
// 指令实际操作方法
this[dir] && this[dir](node, exp)
// 判断是否是事件,
} else if(this.isEvent(attrName)) {
const eventName = attrName.split('@')[1]
node.addEventListener(eventName, () => {
this.$vm.$methods[exp].bind(this.$vm)(e)
})
}
})
}
isEvent(attr) {
return attr.indexOf('@') === 0
}
isDirective(name) {
return name.indexOf('py-') === 0
}
// 双向绑定
model(node, exp) {
this.update(node, exp, 'model')
node.addEventListener('input', (e) => {
this.$vm.$data[exp] = e.target.value
})
}
// 处理事件派发
modelUpdater(node, val) {
node.value = val
}
// k-text对应操作函数
text(node, exp) {
this.update(node, exp, 'text')
}
textUpdater(node, val) {
node.textContent = val
}
html(node, exp) {
this.update(node, exp, 'html')
}
htmlUpdater(node, val) {
node.innerHTML = val
}
// 更新
update(node, exp, type) {
const fn = this[dir + 'Updater']
fn && fn(node, this.$vm[exp])
new Watcher(this.$vm, exp, val => {
fn && fn(node, val)
})
}
}vue3.0数据响应式
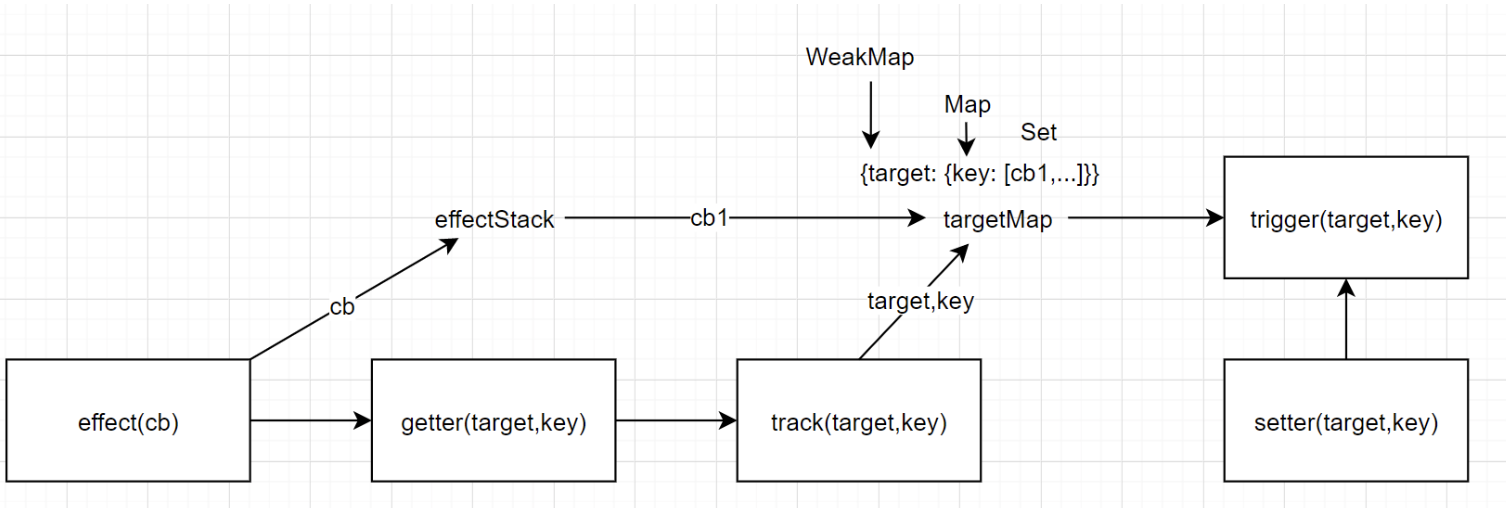
大致的流程
proxy
- 代理对象,set,get,deleteProperty
副作用
- 副作用函数执行,执行过程中,先将副作用函数推入一个栈中
- 执行过程中,如果遇到响应式对象,会触发 proxy 中的 get,get 触发 track
- tack 过程中,会建立,响应式数据的 key 与副作用函数的关系,通过 WeakMap,Map,Set 三级关系
- weakMap 管理的是总的依赖收集对应到 traget, Map 对应的是 target 中的 key,set 对应的是当前 key 对应的副作用列表,此时就建立了,target.key 到 effect 的连接
- 副作用函数第一次执行完毕,函数从副作用函数栈中弹出,结束收集过程
副作用触发过程
- 修改响应式数据,触发 proxy 中的 set,set 触发 trigger,
- trigger 获取对象 target 的 depsMap,然后拿到依赖 depsMap 中 key 的副作用数组,全部执行一遍
核心代码
const isObject = val => val !== null && typeof val === 'object'
function reactive(obj) {
if (!isObject(obj)) {
return obj
}
// Proxy相当于在对象外层加拦截
const observed = new Proxy(obj, {
get(target, key, receiver) {
// Reflect用于执行对象默认操作,更规范、更友好
// Proxy和Object的方法Reflect都有对应
const res = Reflect.get(target, key, receiver)
console.log(`获取${key}:${res}`)
// 依赖收集
track(target, key)
return isObject(res) ? reactive(res) : res
},
set(target, key, value, receiver) {
const res = Reflect.set(target, key, value, receiver)
console.log(`设置${key}:${value}`)
trigger(target, key)
return res
},
deleteProperty(target, key) {
const res = Reflect.deleteProperty(target, key)
console.log(`删除${key}:${res}`)
trigger(target, key)
return res
}
})
return observed
}
const effectStack = []
function effect(fn) {
const rxEffect = function() {
// 1.捕获异常
try {
// 2.入栈
effectStack.push(rxEffect)
// 3.触发依赖收集
return fn()
} finally {
// 4.出栈
effectStack.pop()
}
}
rxEffect()
return rxEffect
}
// 依赖收集,建立target,key和上面的effect函数之间映射关系
// 需要一个数据结构存储该关系
// {target: {key: [cb1, cb2, ...]}}
let targetMap = new WeakMap()
function track(target, key) {
// 获取effect存入的函数
const effect = effectStack[effectStack.length - 1]
if (effect) {
// 获取target对应Map
let depsMap = targetMap.get(target)
if (!depsMap) {
depsMap = new Map()
targetMap.set(target, depsMap)
}
// 获取depsMap中key和其值,也就是Set
let deps = depsMap.get(key)
if (!deps) {
// 首次deps不存在,创建之
deps = new Set()
depsMap.set(key, deps)
}
// 将传入effect,添加到Set里面
deps.add(effect)
console.log(deps)
}
}
function trigger(target, key) {
// 获取映射关系
const depsMap = targetMap.get(target)
if (depsMap) {
// 获取函数集合
const deps = depsMap.get(key)
deps.forEach(effect => {
effect()
})
}
}
const state = reactive({
foo: 'foo',
bar: { a: 1 }
})
effect(() => {
console.log('effect:', state.foo)
})